-40%
ANASTASIUS 491AD Constantinople Follis Authentic Medieval Byzantine Coin i59265
$ 68.64
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i59265
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Byzantine Empire
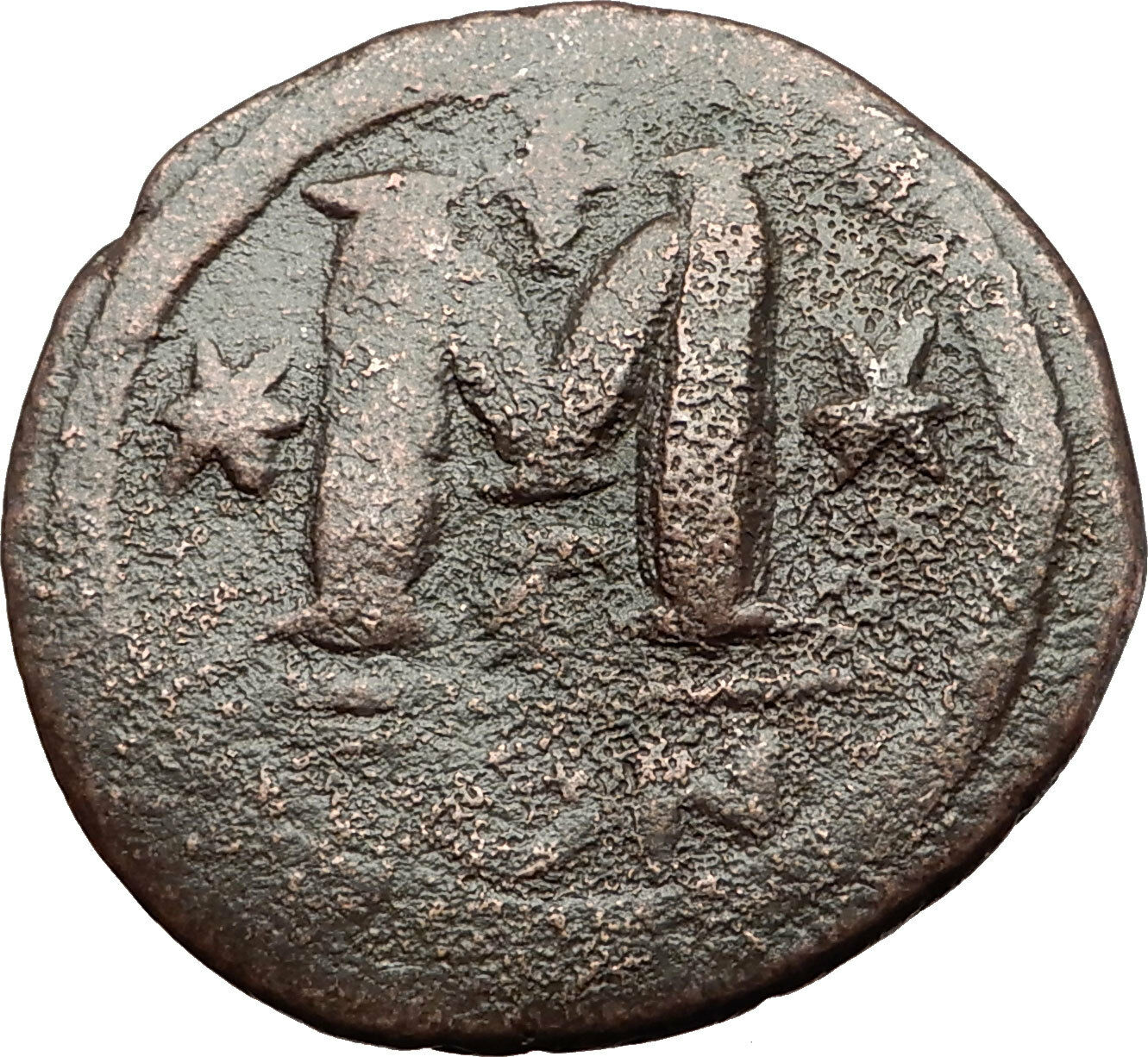
Anastasius I - Emperor: April 11, 491 A.D. - July 1, 518 A.D.
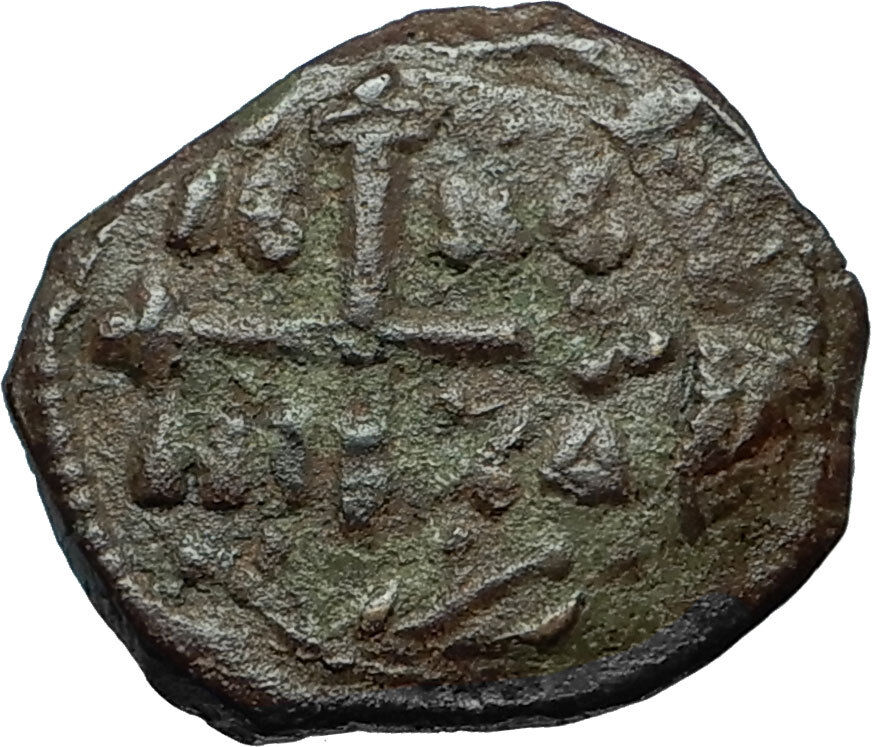
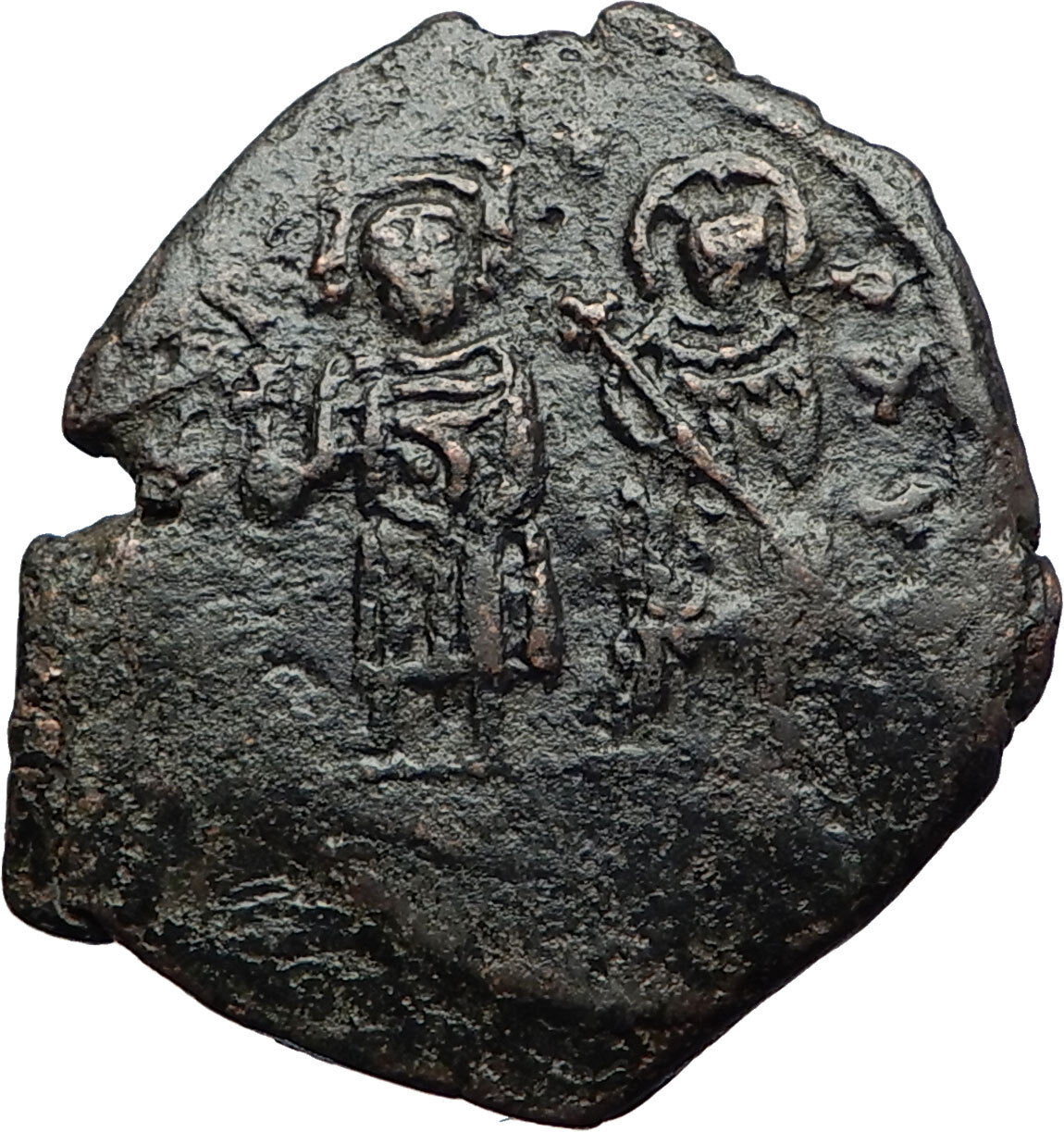
Bronze Follis 35mm (15.35 grams) Constantinople mint: 491-518 A.D.
Reference: Sear 21
D N ANASTASIVS PP AVG - Diademed, draped and cuirassed bust right.
Large M between two stars; above, cross; beneath, officina letter; in exergue, CON.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Anastasius I
(
Latin
:
Flavius Anastasius Dicorus Augustus
,
Greek
:
Ἀναστάσιος
; c. 431 – 9 July 518) was
Byzantine Emperor
from 491 to 518. During his reign the Roman eastern frontier underwent extensive re-fortification, including the construction of
Dara
, a stronghold intended to counter the Persian fortress of
Nisibis
. During his reign was built one of the most fortified castle cities on the Adriatic
Durrës Castle
in
Durrës
.
Background and personal characteristics
Anastasius was born at
Dyrrhachium
in the Latin-speaking part of the Balkans; the date is unknown, but he is thought to have been born no later than 430 or 431. He was born into an
Illyrian
family, the son of Pompeius (born
c
. 410), nobleman of Dyrrachium, and wife Anastasia Constantina (born
c
. 410). His mother was an
Arian
, sister of Clearchus, also an Arian, and a paternal granddaughter of Gallus (born
c
. 370), son of Anastasia (born
c
. 352) and husband, in turn daughter of Flavius Claudius
Constantius Gallus
and wife and cousin
Constantina
.
Anastasius had one eye black and one eye blue (
heterochromia
), and for that reason he was nicknamed
Dicorus
(Greek: Δίκορος, "two-
pupiled
").
Accession
At the time of the death of
Zeno
(491), Anastasius, a palace official (
silentiarius
), held a very high character, and was raised to the throne of the Eastern Roman Empire by
Ariadne
, Zeno's widow, who preferred him to Zeno's brother,
Longinus
.
Ariadne married him shortly after his accession on 20 May 491. His reign, though afterwards disturbed by foreign and internecine wars and religious distractions, commenced auspiciously. He gained the popular favour by a judicious remission of taxation, and displayed great vigour and energy in administering the affairs of the Empire.
Foreign policy and wars
Anastasius engaged in the
Isaurian War
against the usurper
Longinus
and the
Anastasian War
against Sassanid Persia.
The Isaurian War (492-497) was stirred up by the
Isaurian
supporters of Longinus, the brother of Zeno who was passed over in his succession in favor of Anastasius. The
battle of Cotyaeum
in 492 "broke the back" of the revolt, but
guerrilla warfare
continued in the Isaurian mountains for some years longer.
In the
Anastasian War
(502–505),
Theodosiopolis
and
Amida
were captured by the Sassanids, but Persian provinces also suffered severely and the Byzantines recovered Amida. Both adversaries were exhausted when peace was made in 506 on the basis of the status quo. Anastasius afterwards built the strong fortress of
Daras
to hold the Persians in check in
Nisibis
. The
Balkan
provinces were left denuded of troops, however, and were devastated by invasions of
Slavs
and
Bulgars
; to protect
Constantinople
and its vicinity against them, the emperor built the
Anastasian Wall
, extending from the
Propontis
to the
Euxine
.
Domestic and ecclesiastical policies
The Emperor was a convinced
Miaphysite
, following the teachings of
Cyril of Alexandria
and
Severus of Antioch
who taught "One Incarnate Nature of Christ" in an undivided union of the Divine and human natures, but his ecclesiastical policy was moderate; he endeavoured to maintain the principle of the
Henotikon
of Zeno and the peace of the church. It was rebellious demonstrations of the Byzantine populace, that drove him in 512 to abandon this policy and adopt Miaphysitic programme. His consequent unpopularity in the European provinces was utilized by an ambitious man, named
Vitalian
, to organize a dangerous rebellion, in which he was assisted by a horde of "
Huns
" (514–515); it was finally suppressed by a naval victory won by the general
Marinus
.
Successor
The
Anonymous Valesianus
tells an account about his choosing of a successor: Anastasius could not decide which of his three nephews should succeed him, so he put a message under a couch and had his nephews take seats in the room, which also had two other seats; he believed that the nephew to sit on the special couch would be his proper heir. However, two of his nephews sat on the same couch, and the one with the concealed message remained empty.
Then, after putting the matter to God in
prayer
, he determined that the first person to enter his room the next morning should be the next Emperor, and that person was
Justin
, the chief of his guards. In fact, Anastasius probably never thought of Justin as a successor, but the issue was decided for him after his death. At the end of his reign, he left the Imperial treasury richer by 23,000,000
solidi
or 320,000 pounds of gold.
Anastasius died childless in Constantinople on 9 July 518 (some sources say 8 or 10 July) and was buried at the
Church of the Holy Apostles
.
Family
Anastasius is known to have had a brother named
Flavius Paulus
, who served as
Roman consul
in 496. A sister-in-law, known as Magna, was mother to Irene and mother-in-law to
Olybrius
. This Olybrius was son of
Anicia Juliana
and
Areobindus Dagalaiphus Areobindus
. The daughter of Olybrius and Irene was named Proba. She married Probus and was mother to a younger Juliana. This younger Juliana married another Anastasius and was mother of Areobindus, Placidia, and a younger Proba. Another nephew of Anastasius was
Flavius Probus
, Roman consul in 502. Caesaria, sister of Anastasius, married Secundinus. They were parents to
Hypatius
and
Pompeius
. Flavius
Anastasius Paulus Probus Moschianus Probus Magnus
, Roman Consul in 518 also was a great-nephew of Anastasius. His daughter Juliana later married
Marcellus
, a brother of
Justin II
. The extensive family may well have included viable candidates for the throne.
Byzantine Empire coinage reform
The main elements of the complex monetary system of the early Byzantine Empire, which suffered a partial collapse in the 5th century, were revived by Emperor Anastasius I (491–518) in 498. The new system involved three denominations of gold (the solidus and its half and third) and five of copper (the follis, worth 40 nummi and its fractions down to a nummus).
A 40 nummi coin of Anastasius is depicted on the
obverse
of the
Macedonian
50
denars
banknote, issued in 1996.
Anastasius I Dicorus
Leonid Dynasty
Born:
c. 430
Died:
9 July 518
Regnal titles
Preceded by
Zeno
Byzantine Emperor
491–518
Succeeded by
Justin I
Political offices
Preceded by
Anicius Olybrius
(alone)
Consul
of the
Roman Empire
492
with Flavius Rufus
Succeeded by
Flavius Albinus Iunior
,
Flavius Eusebius
II
Preceded by
Paulus
,
Post consulatum Viatoris
(West)
Consul
of the
Roman Empire
497
Succeeded by
Paulinus
,
John the Scythian
Preceded by
Flavius Ennodius Messala
,
Areobindus Dagalaiphus Areobindus
Consul
of the
Roman Empire
507
with
Venantius
iunior
Clovis I
Succeeded by
Basilius Venantius
,
Celer
The
Byzantine Empire
, or
Eastern Roman Empire
, was the predominantly
Greek
-speaking eastern half continuation and remainder of the
Roman Empire
during
Late Antiquity
and the
Middle Ages
. Its capital city was
Constantinople
(modern-day
Istanbul
), originally founded as
Byzantium
. It survived the
fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire
in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it
fell
to the
Ottoman Turks
in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the
Roman Empire
(
Ancient Greek
:
Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων
,
tr.
Basileia Rhōmaiōn
;
Latin
:
Imperium Romanum
), or
Romania
(
Ῥωμανία
), and to themselves as "Romans".
Several events from the 4th to 6th centuries mark the transitional period during which the Roman Empire's
east and west
divided
. In 285, the
emperor
Diocletian
(r. 284–305) partitioned the Roman Empire's administration into eastern and western halves. Between 324 and 330,
Constantine I
(r. 306–337) transferred the main capital from
Rome
to
Byzantium
, later known as
Constantinople
("City of Constantine") and
Nova Roma
("New Rome"). Under
Theodosius I
(r. 379–395),
Christianity
became the Empire's official
state religion
and others such as
Roman polytheism
were
proscribed
. And finally, under the reign of
Heraclius
(r. 610–641), the Empire's military and administration were restructured and adopted Greek for official use instead of Latin. Thus, although it continued the Roman state and maintained Roman state traditions, modern historians distinguish
Byzantium
from
ancient Rome
insofar as it was oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by
Orthodox Christianity
rather than
Roman polytheism
.
The borders of the Empire evolved significantly over its existence, as it went through several cycles of decline and recovery. During the reign of
Justinian I
(r. 527–565), the Empire reached its greatest extent after reconquering much of the historically Roman western
Mediterranean
coast, including north Africa, Italy, and Rome itself, which it held for two more centuries. During the reign of
Maurice
(r. 582–602), the Empire's eastern frontier was expanded and the north stabilised. However, his assassination caused a
two-decade-long war
with
Sassanid Persia
which exhausted the Empire's resources and contributed to major territorial losses during the
Muslim conquests
of the 7th century. In a matter of years the Empire lost its richest provinces, Egypt and Syria, to the Arabs.
During the
Macedonian dynasty
(10th–11th centuries), the Empire again expanded and experienced a two-century long
renaissance
, which came to an end with the loss of much of Asia Minor to the
Seljuk Turks
after the
Battle of Manzikert
in 1071. This battle opened the way for the Turks to settle in
Anatolia
as a homeland.
The final centuries of the Empire exhibited a general trend of decline. It struggled to
recover during the 12th century
, but was delivered a mortal blow during the
Fourth Crusade
, when Constantinople was sacked and the Empire
dissolved and divided
into competing Byzantine Greek and
Latin realms
. Despite the eventual recovery of Constantinople and
re-establishment of the Empire in 1261
, Byzantium remained only one of several small rival states in the area for the final two centuries of its existence. Its remaining territories were
progressively annexed by the Ottomans
over the 15th century. The
Fall of Constantinople
to the
Ottoman Empire
in 1453 finally ended the Byzantine Empire.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "Guide on How to Use My Store" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.
You may also want to do a YouTube search for the term "ancient coin collecting" for educational videos on this topic.