-40%
540 Justinian I Byzantine Dated Follis Constantinople Mint NGC VF (19081201C)
$ 155.76
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
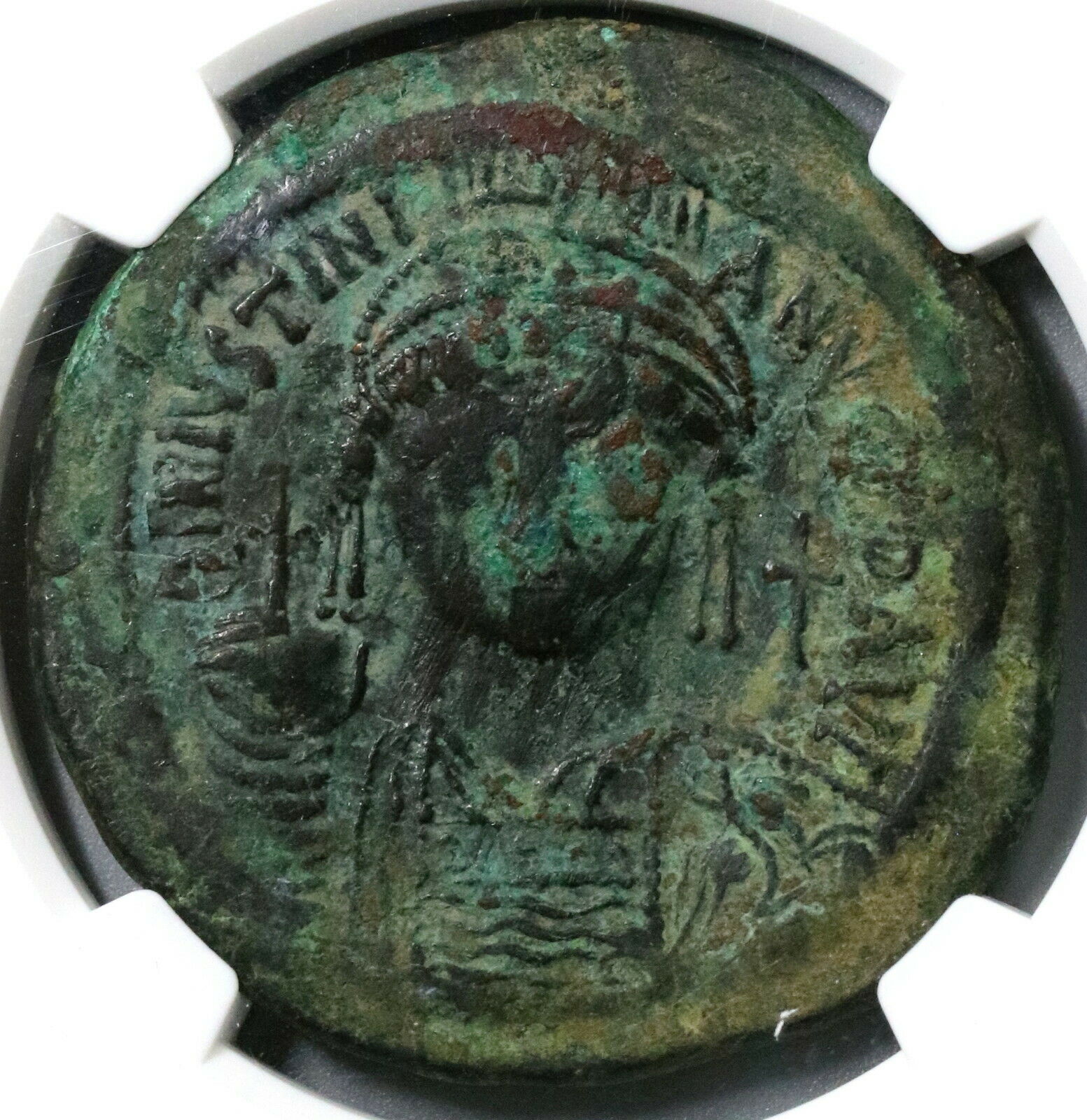
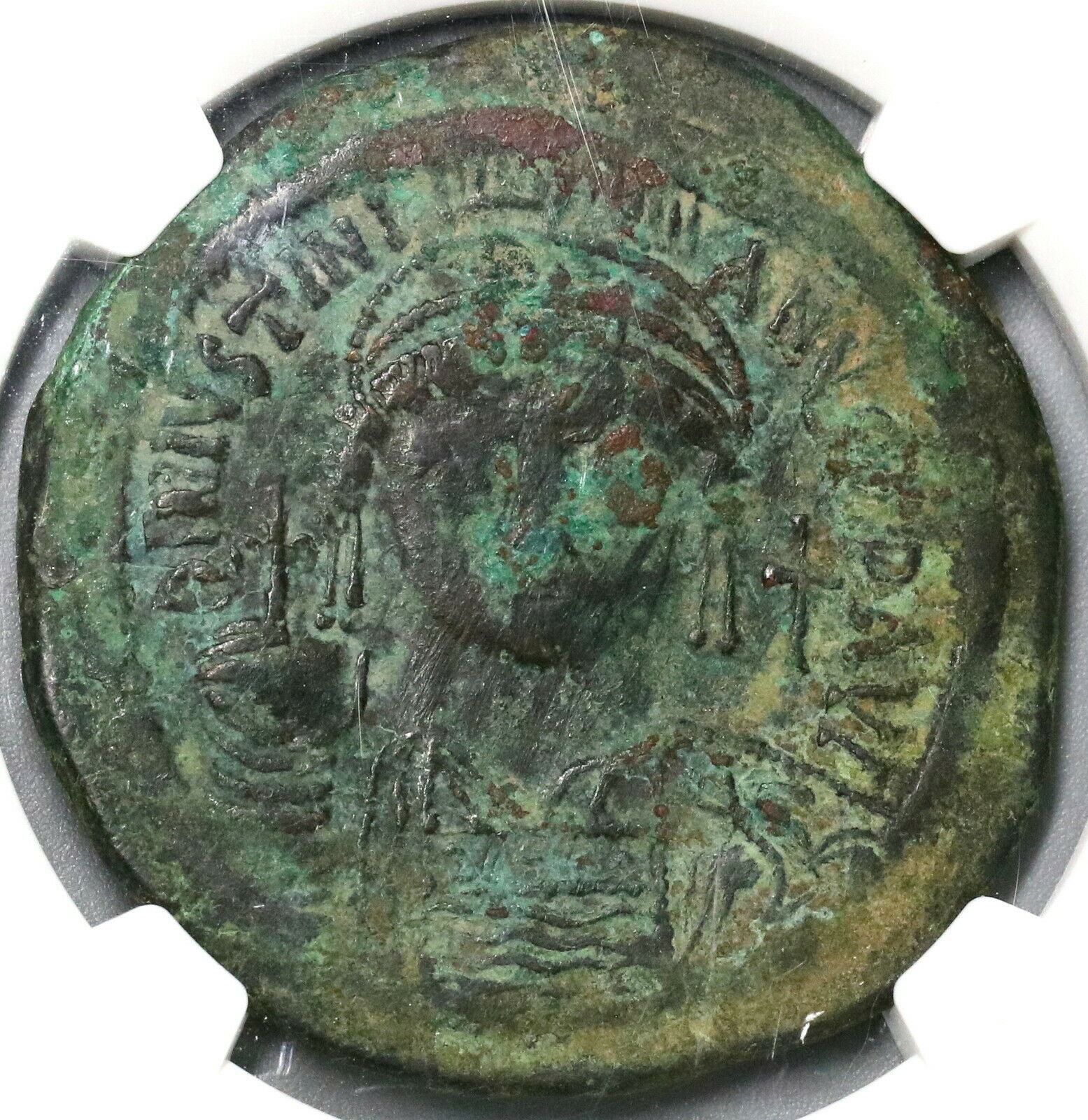
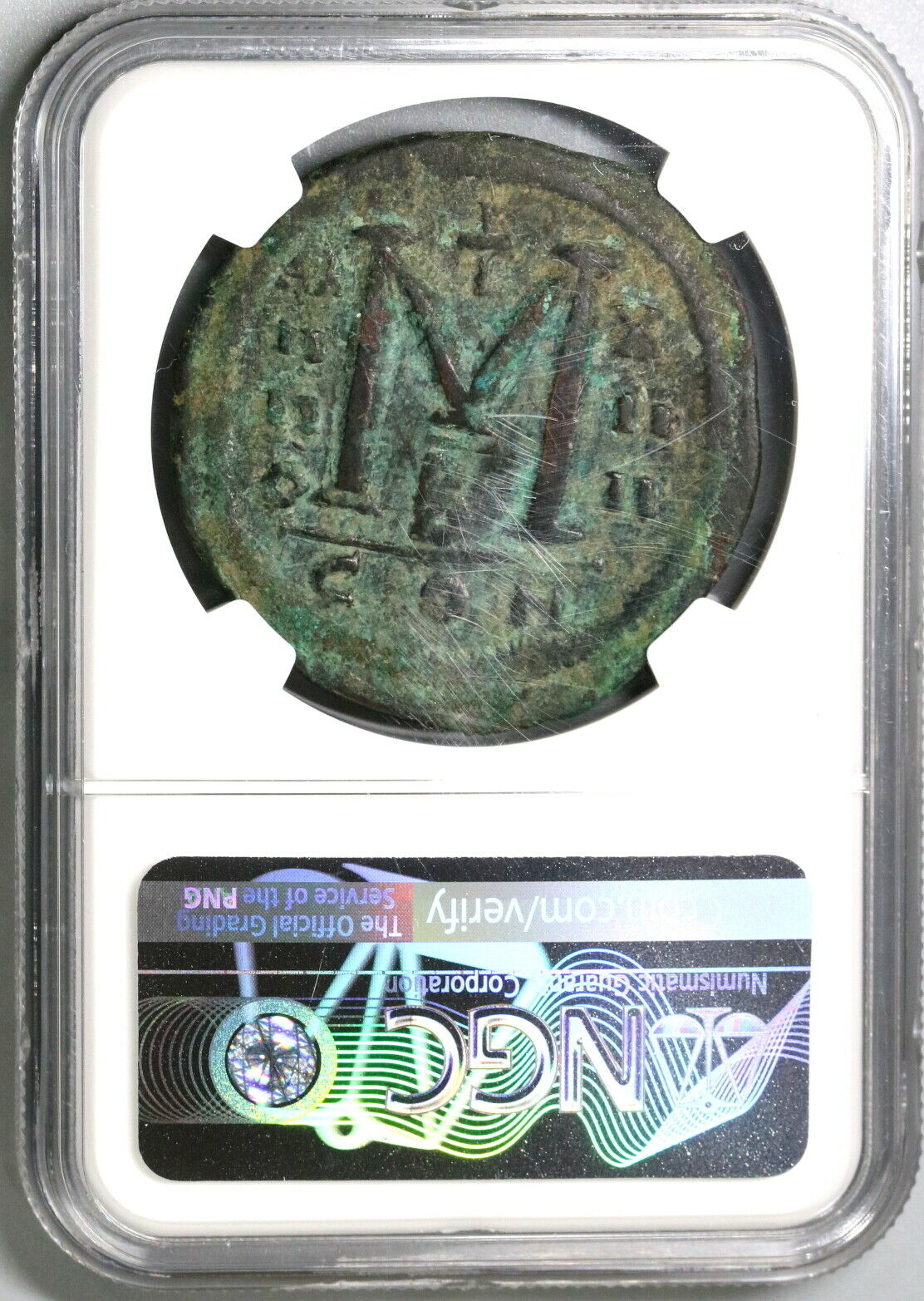
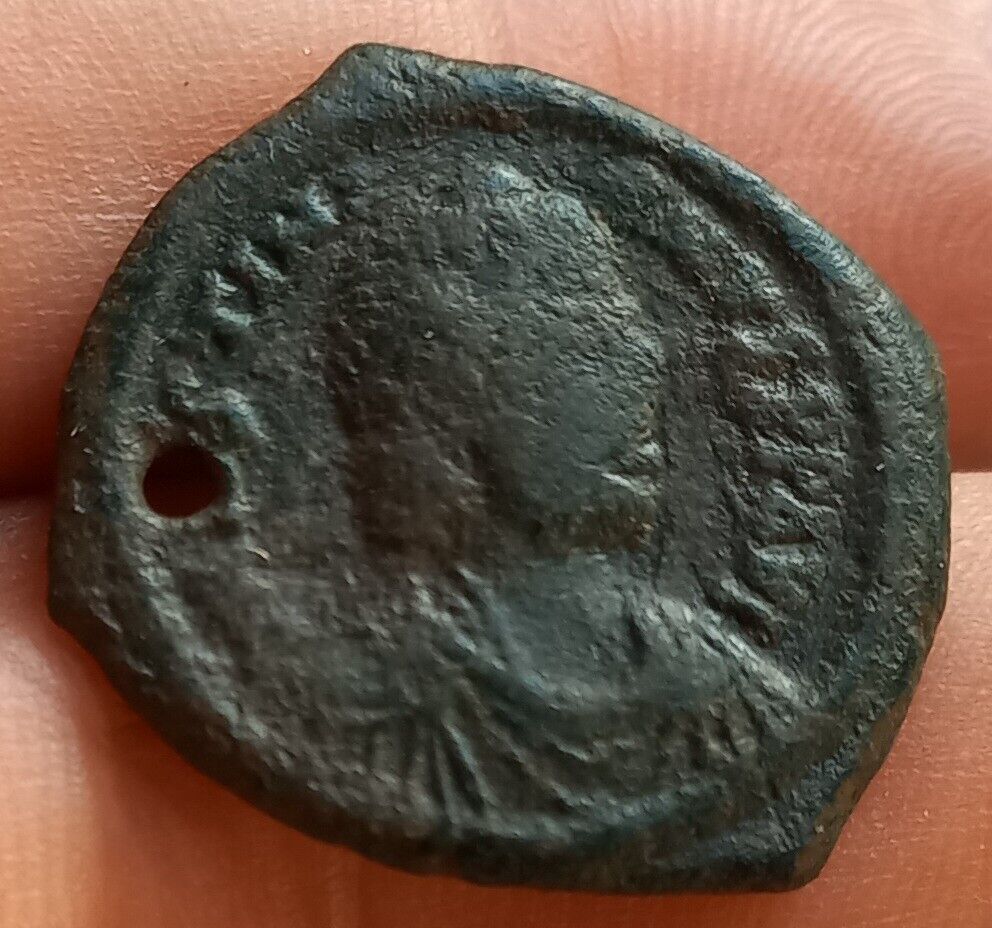
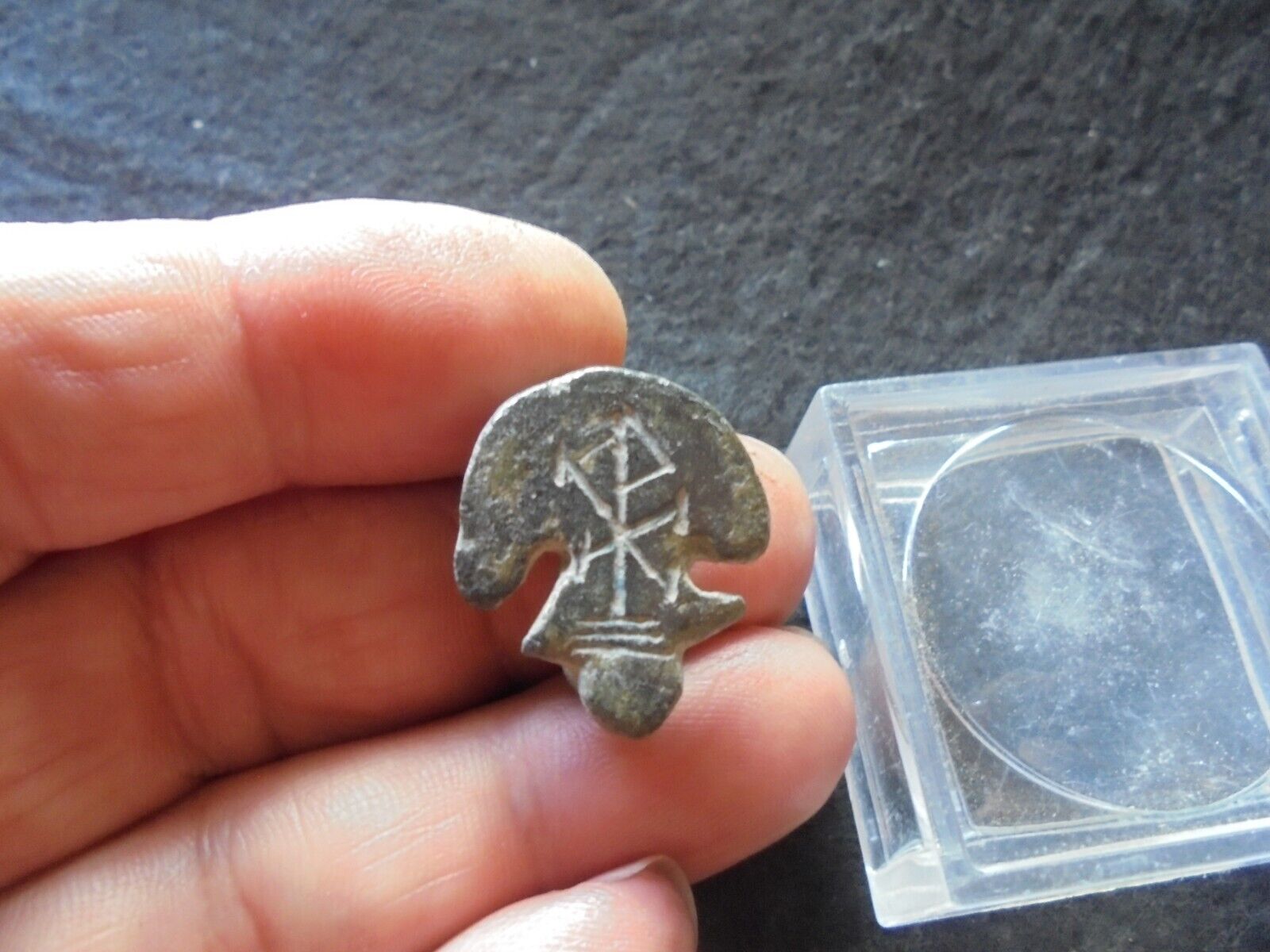
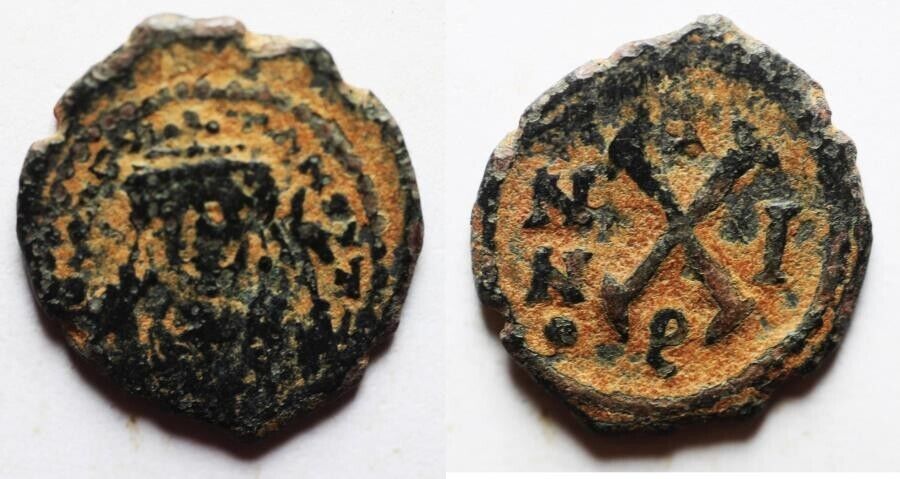
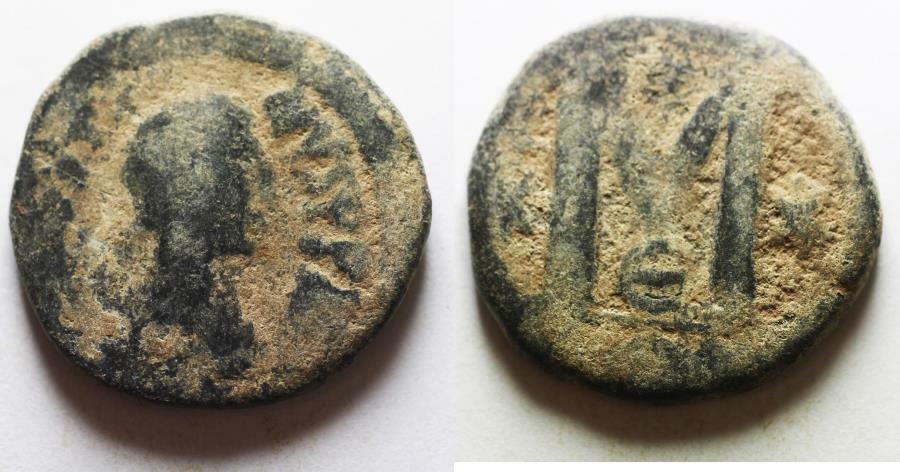
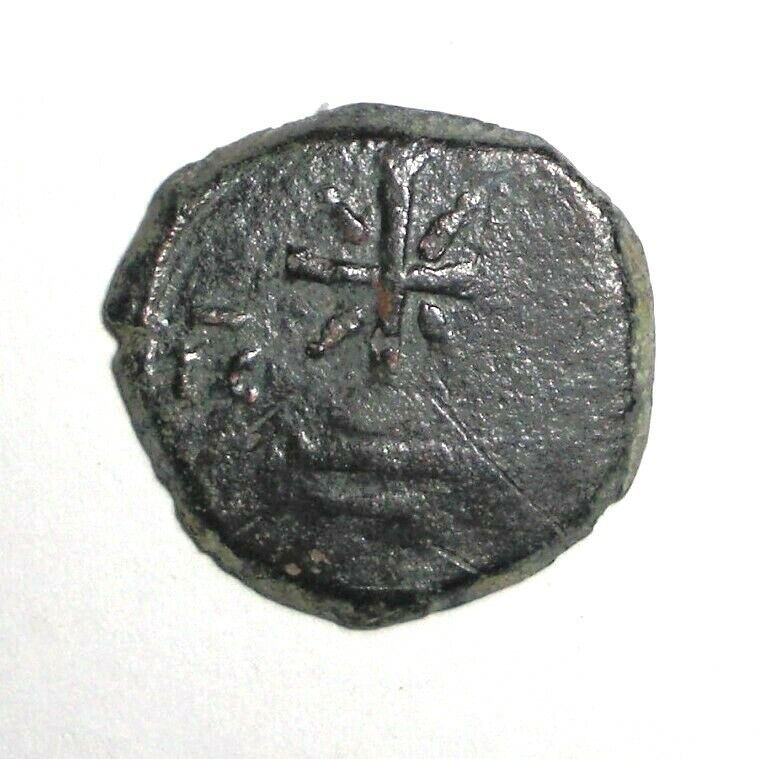
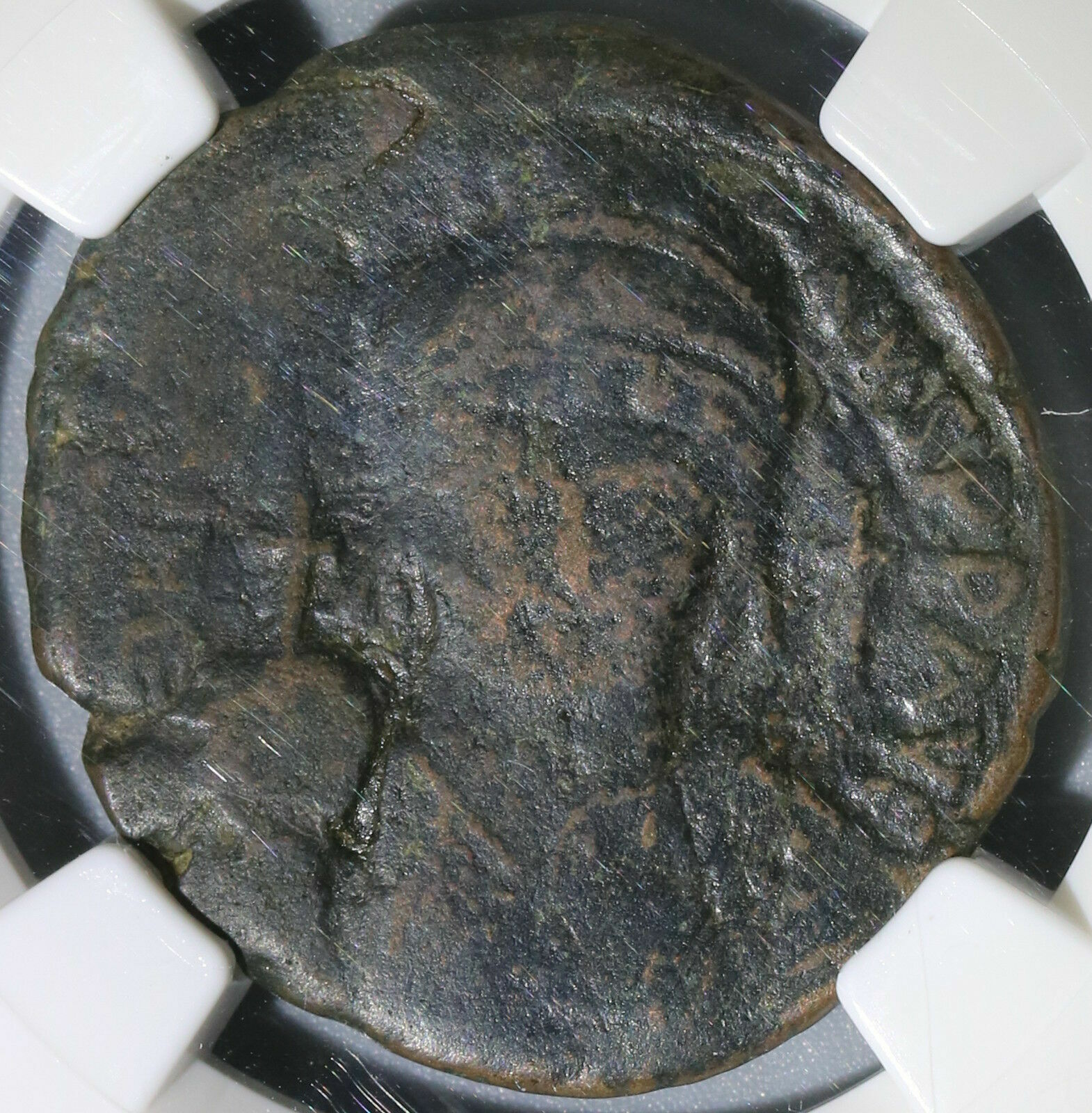
Dated Emperor Justinian I Byzantine Empire follis coin.
Large copper coin, approx 40mm, 22.7g.
Sear 163.
Well struck and centered with full legends.
Obverse: D N IVSTINIANVS PP AVG, Helmeted and cuirassed bust facing holding gl cr and shield, to right cross.
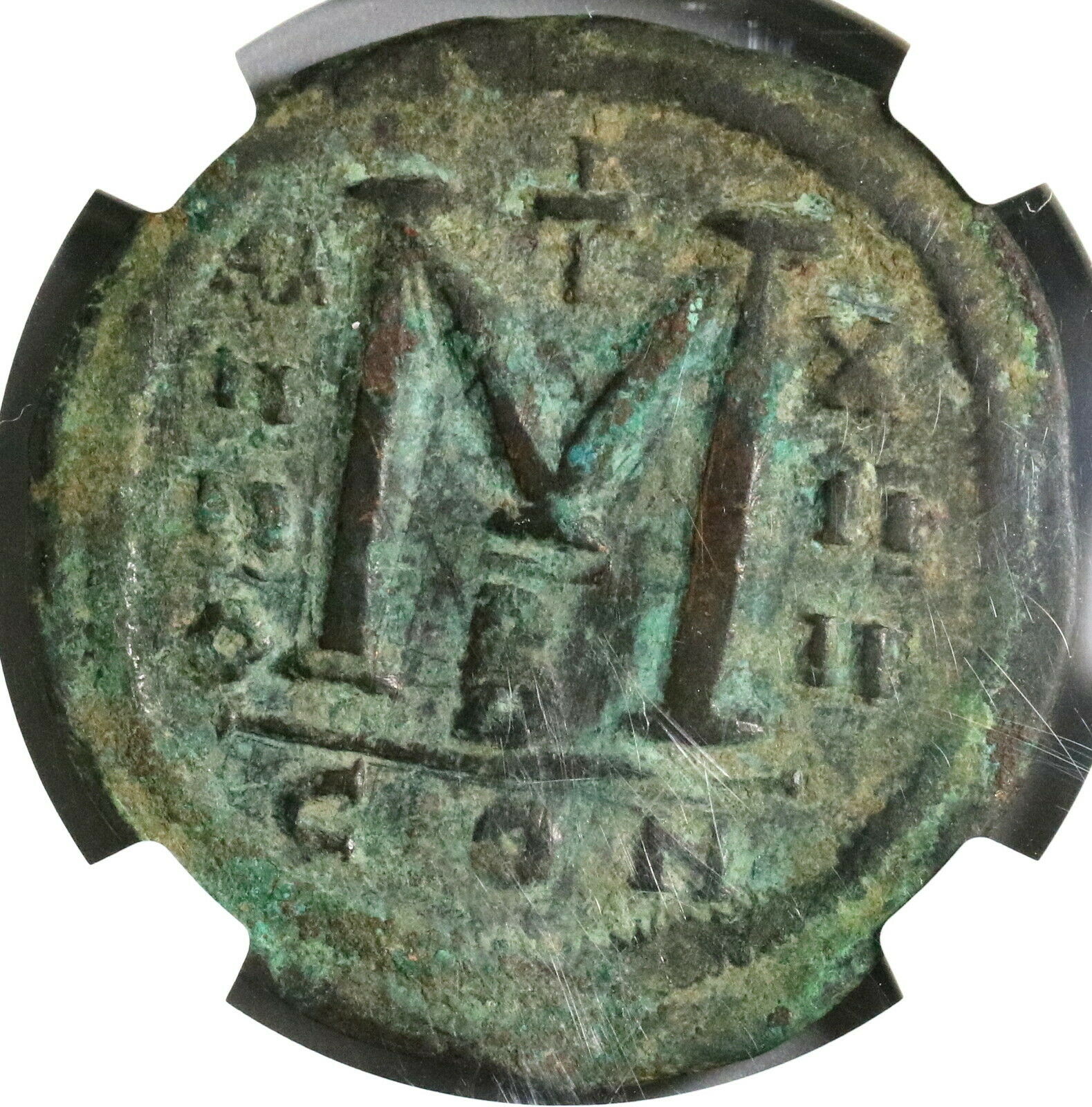
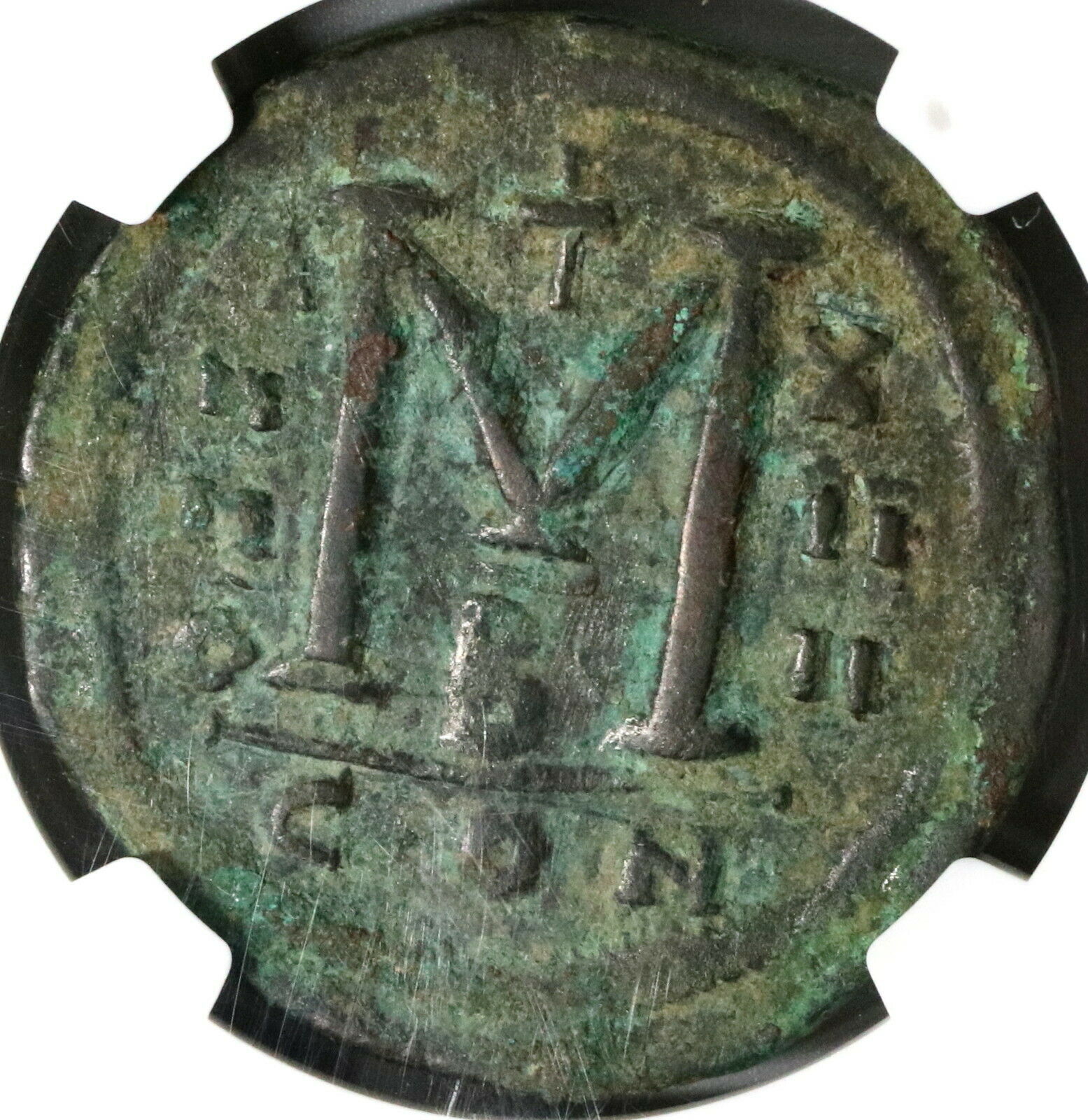
Reverse: Demonation M nummia = 1 follis,
Constantinople mint (CON), officinia B, reign year ANNO XIIII (14) = 540/1 CE.
Certified by NGC to VF, Strike 5/5, Surface 2/5.
Justinian the Great was the Eastern Roman emperor from 527 to 565. During his reign, Justinian sought to revive the empire's greatness and reconquer the lost western half of the historical Roman Empire. Justinian's rule constitutes a distinct epoch in the history of the Later Roman empire, and his reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized renovatio imperii, or "restoration of the Empire".
Because of his restoration activities, Justinian has sometimes been known as the "last Roman" in modern historiography. This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million solidi.
A still more resonant aspect of his legacy was the uniform rewriting of Roman law, the Corpus Juris Civilis, which is still the basis of civil law in many modern states.
His reign also marked a blossoming of Byzantine culture, and his building program yielded such masterpieces as the church of Hagia Sophia.
A devastating outbreak of bubonic plague in the early 540s marked the end of an age of splendour.